Function that calculates, for a specified node pair representing endpoints, path statistics from a sparse precision matrix. The sparse precision matrix is taken to represent the conditional independence graph of a Gaussian graphical model. The contribution to the observed covariance between the specified endpoints is calculated for each (heuristically) determined path between the endpoints.
GGMpathStats(
P0,
node1,
node2,
neiExpansions = 2,
verbose = TRUE,
graph = TRUE,
nrPaths = 2,
lay = "layout_in_circle",
coords = NULL,
nodecol = "skyblue",
Vsize = 15,
Vcex = 0.6,
VBcolor = "darkblue",
VLcolor = "black",
all.edges = TRUE,
prune = TRUE,
legend = TRUE,
scale = 1,
Lcex = 0.8,
PTcex = 2,
main = ""
)Arguments
- P0
Sparse (possibly standardized) precision matrix.
- node1
A
numericspecifying an endpoint. The numeric should correspond to a row/column of the precision matrix and as such represents the corresponding variable.- node2
A
numericspecifying a second endpoint. The numeric should correspond to a row/column of the precision matrix and as such represents the corresponding variable.- neiExpansions
A
numericdetermining how many times the neighborhood around the respective endpoints should be expanded in the search for shortest paths between the node pair.- verbose
A
logicalindicating if a summary of the results should be printed on screen.- graph
A
logicalindicating if the strongest paths should be visualized with a graph.- nrPaths
A
numericindicating the number of paths (with the highest contribution to the marginal covariance between the indicated node pair) to be visualized/highlighted.- lay
A
charactermimicking a call toigraphlayout functions. Determines the placement of vertices.- coords
A
matrixcontaining coordinates. Alternative to the lay-argument for determining the placement of vertices.- nodecol
A
characterdetermining the color ofnode1andnode2.- Vsize
A
numericdetermining the vertex size.- Vcex
A
numericdetermining the size of the vertex labels.- VBcolor
A
characterdetermining the color of the vertex borders.- VLcolor
A
characterdetermining the color of the vertex labels.- all.edges
A
logicalindicating if edges other than those implied by thenrPaths-paths betweennode1and node2 should also be visualized.- prune
A
logicaldetermining if vertices of degree 0 should be removed.- legend
A
logicalindicating if the graph should come with a legend.- scale
A
numericrepresenting a scale factor for visualizing strenght of edges. It is a relative scaling factor, in the sense that the edges implied by thenrPaths-paths betweennode1and node2 have edge thickness that is twice this scaling factor (so it is a scaling factor vis-a-vis the unimplied edges).- Lcex
A
numericdetermining the size of the legend box.- PTcex
A
numericdetermining the size of the exemplary lines in the legend box.- main
A
charactergiving the main figure title.
Value
An object of class list:
- pathStats
A
matrixspecifying the paths, their respective lengths, and their respective contributions to the marginal covariance between the endpoints.- paths
A
listrepresenting the respective paths as numeric vectors.- Identifier
A
data.framein which each numeric frompathsis connected to an identifier such as a variable name.
Details
The conditional independence graph (as implied by the sparse precision
matrix) is undirected. In undirected graphs origin and destination are
interchangeable and are both referred to as 'endpoints' of a path. The
function searches for shortest paths between the specified endpoints
node1 and node2. It searches for shortest paths that visit
nodes only once. The shortest paths between the provided endpoints are
determined heuristically by the following procedure. The search is initiated
by application of the get.all.shortest.paths-function from the
igraph-package, which yields all shortest paths between the
nodes. Next, the neighborhoods of the endpoints are defined (excluding the
endpoints themselves). Then, the shortest paths are found between: (a)
node1 and node Vs in its neighborhood; (b) node Vs in
the node1-neighborhood and node Ve in the
node2-neighborhood; and (c) node Ve in the
node2-neighborhood and node2. These paths are glued and new
shortest path candidates are obtained (preserving only novel paths). In
additional iterations (specified by neiExpansions) the node1-
and node2-neighborhood are expanded by including their neighbors
(still excluding the endpoints) and shortest paths are again searched as
described above.
The contribution of a particular path to the observed covariance between the
specified node pair is calculated in accordance with Theorem 1 of Jones and
West (2005). As in Jones and West (2005), paths whose weights have an
opposite sign to the marginal covariance (between endnodes of the path) are
referred to as 'moderating paths' while paths whose weights have the same
sign as the marginal covariance are referred to as 'mediating' paths. Such
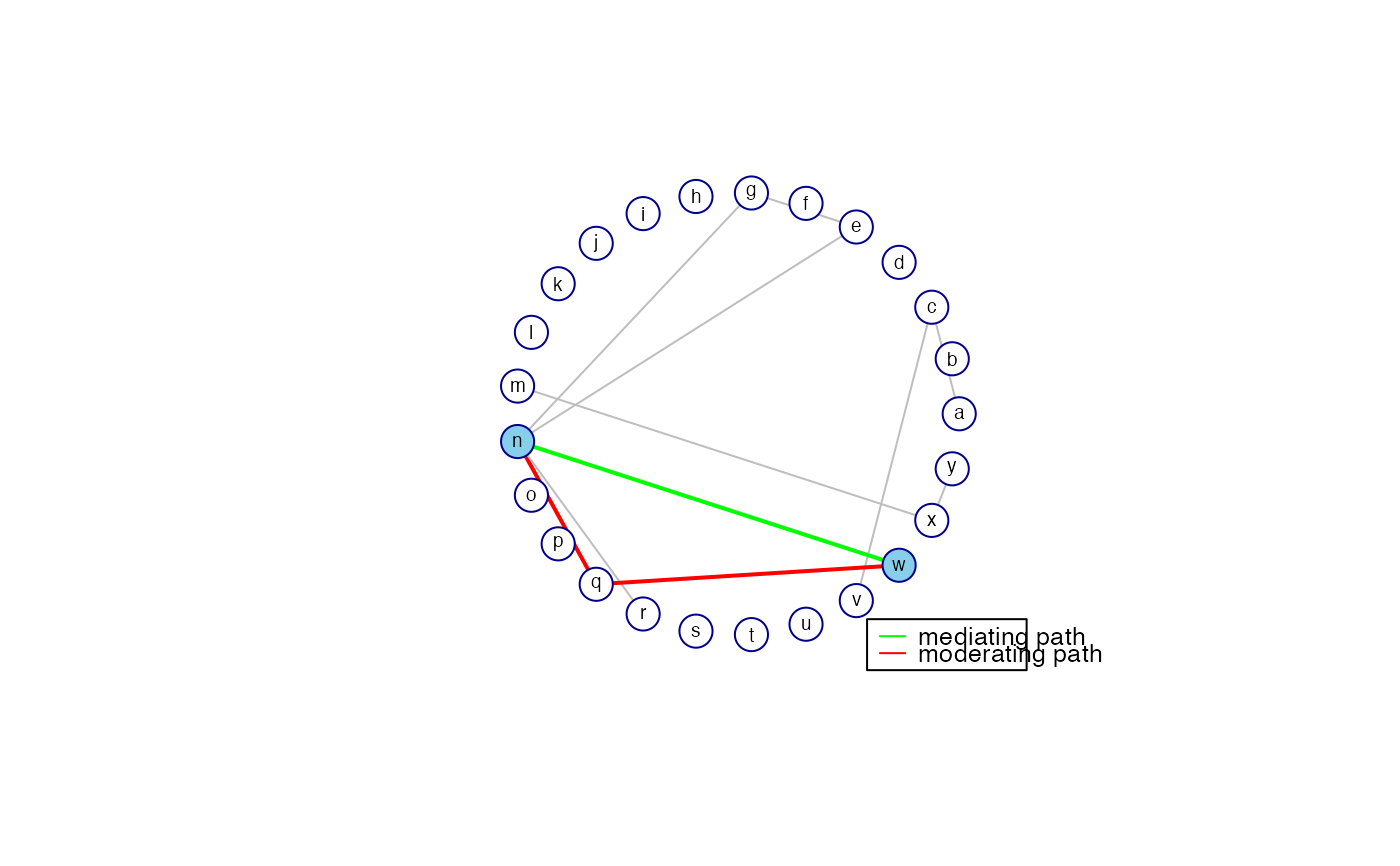
paths are visualized when graph = TRUE.
All arguments following the graph argument are only (potentially)
used when graph = TRUE. When graph = TRUE the conditional
independence graph is returned with the paths highlighted that have the
highest contribution to the marginal covariance between the specified
endpoints. The number of paths highlighted is indicated by nrPaths.
The edges of mediating paths are represented in green while the edges of
moderating paths are represented in red. When all.edges = TRUE the
edges other than those implied by the nrPaths-paths between
node1 and node2 are also visualized (in lightgrey). When
all.edges = FALSE only the mediating and moderating paths implied by
nrPaths are visualized.
The default layout gives a circular placement of the vertices. Most layout
functions supported by igraph are supported (the function is
partly a wrapper around certain igraph functions). The igraph
layouts can be invoked by a character that mimicks a call to a
igraph layout functions in the lay argument. When using
lay = NULL one can specify the placement of vertices with the
coords argument. The row dimension of this matrix should equal the
number of (pruned) vertices. The column dimension then should equal 2 (for
2D layouts) or 3 (for 3D layouts). The coords argument can also be
viewed as a convenience argument as it enables one, e.g., to layout a graph
according to the coordinates of a previous call to Ugraph. If both
the the lay and the coords arguments are not NULL, the lay argument
takes precedence
The arguments Lcex and PTcex are only used when legend =
TRUE. If prune = TRUE the vertices of degree 0 (vertices not
implicated by any edge) are removed. For the colors supported by the
arguments nodecol, Vcolor, and VBcolor, see
https://www.nceas.ucsb.edu/sites/default/files/2020-04/colorPaletteCheatsheet.pdf.
Note
Eppstein (1998) describes a more sophisticated algorithm for finding the top k shortest paths in a graph.
References
Eppstein, D. (1998). Finding the k Shortest Paths. SIAM Journal on computing 28: 652-673.
Jones, B., and West, M. (2005). Covariance Decomposition in Undirected Gaussian Graphical Models. Biometrika 92: 779-786.
See also
Examples
## Obtain some (high-dimensional) data
p <- 25
n <- 10
set.seed(333)
X <- matrix(rnorm(n*p), nrow = n, ncol = p)
colnames(X) <- letters[1:p]
## Obtain regularized precision under optimal penalty
OPT <- optPenalty.LOOCVauto(X, lambdaMin = .5, lambdaMax = 30)
## Determine support regularized standardized precision under optimal penalty
PC0 <- sparsify(OPT$optPrec, threshold = "localFDR")$sparseParCor
#> Step 1... determine cutoff point
#> Step 2... estimate parameters of null distribution and eta0
#> Step 3... compute p-values and estimate empirical PDF/CDF
#> Step 4... compute q-values and local fdr
#> Step 5... prepare for plotting
 #>
#> - Retained elements: 11
#> - Corresponding to 3.67 % of possible edges
#>
## Obtain information on mediating and moderating paths between nodes 14 and 23
pathStats <- GGMpathStats(PC0, 14, 23, verbose = TRUE, prune = FALSE)
#> Covariance between node pair : 0.06757
#> ----------------------------------------
#> path length contribution
#> 1 14--23 1 0.07211
#> 2 14--17--23 2 -0.00453
#> ----------------------------------------
#> Sum path contributions : 0.06757
#> Warning: 'as.is' should be specified by the caller; using TRUE
#> Warning: 'as.is' should be specified by the caller; using TRUE
#>
#> - Retained elements: 11
#> - Corresponding to 3.67 % of possible edges
#>
## Obtain information on mediating and moderating paths between nodes 14 and 23
pathStats <- GGMpathStats(PC0, 14, 23, verbose = TRUE, prune = FALSE)
#> Covariance between node pair : 0.06757
#> ----------------------------------------
#> path length contribution
#> 1 14--23 1 0.07211
#> 2 14--17--23 2 -0.00453
#> ----------------------------------------
#> Sum path contributions : 0.06757
#> Warning: 'as.is' should be specified by the caller; using TRUE
#> Warning: 'as.is' should be specified by the caller; using TRUE
 pathStats
#> $pathStats
#> length contribution
#> 14--23 1 0.072107147
#> 14--17--23 2 -0.004533757
#>
#> $paths
#> $paths$`14--23`
#> + 2/25 vertices, named, from 1977cf0:
#> [1] 14 23
#>
#> $paths$`14--17--23`
#> + 3/25 vertices, named, from 1977cf0:
#> [1] 14 17 23
#>
#>
#> $Identifier
#> Numeric VarName
#> 1 1 a
#> 2 2 b
#> 3 3 c
#> 4 4 d
#> 5 5 e
#> 6 6 f
#> 7 7 g
#> 8 8 h
#> 9 9 i
#> 10 10 j
#> 11 11 k
#> 12 12 l
#> 13 13 m
#> 14 14 n
#> 15 15 o
#> 16 16 p
#> 17 17 q
#> 18 18 r
#> 19 19 s
#> 20 20 t
#> 21 21 u
#> 22 22 v
#> 23 23 w
#> 24 24 x
#> 25 25 y
#>
pathStats
#> $pathStats
#> length contribution
#> 14--23 1 0.072107147
#> 14--17--23 2 -0.004533757
#>
#> $paths
#> $paths$`14--23`
#> + 2/25 vertices, named, from 1977cf0:
#> [1] 14 23
#>
#> $paths$`14--17--23`
#> + 3/25 vertices, named, from 1977cf0:
#> [1] 14 17 23
#>
#>
#> $Identifier
#> Numeric VarName
#> 1 1 a
#> 2 2 b
#> 3 3 c
#> 4 4 d
#> 5 5 e
#> 6 6 f
#> 7 7 g
#> 8 8 h
#> 9 9 i
#> 10 10 j
#> 11 11 k
#> 12 12 l
#> 13 13 m
#> 14 14 n
#> 15 15 o
#> 16 16 p
#> 17 17 q
#> 18 18 r
#> 19 19 s
#> 20 20 t
#> 21 21 u
#> 22 22 v
#> 23 23 w
#> 24 24 x
#> 25 25 y
#>